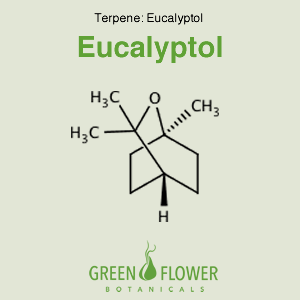
Eucalyptol – Terpene
Description:
EFFECTS: Anti-Alzheimer’s, Anti-Asthma, Anti-bacterial, Anti-cancer, Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant.
Strains containing Eucalyptol include: ACDC.
Eucalyptol, also known as 1,8 cineole, has a fresh, strong eucalyptus, camphoraceous, minty odor. It is a cyclic ether monoterpene. Eucalyptol has been popularly used on the skin, gums, or other topical areas. The terpene is toxic to several species of bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus. Further research has proven eucalyptol to be a potential treatment for Alzheimer’s, as it lowered the inflammation caused by amyloid beta plaques. eucalyptol is also an anti-inflammatory for sinuses and the digestive system. As an antioxidant, eucalyptol was effective at preventing lipid oxidation. In addition, eucalyptol has been effective in battling leukemia and colon cancer cells. Asthma remedies have also been used with eucalyptol.
⇩ View A – Z Index of Terpenes ⇩
Effects
Anti-Alzheimer’s
Anti-Asthma
Anti-bacterial
Anti-cancer
Anti-inflammatory
Antioxidant
Research
Anti-bacterial
Eucalyptol demonstrated bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Serratia marcescens, and Staphylococcus aureus, proving to be a good anti-bacterial agent.
Alzheimer’s
Eucalyptol was used as treatment against PC12 brain cells exposed to amyloid beta plaques. Molecular analysis showed the terpene lowered the expression of NOS-2, COX-2 and NF-κB. In addition on the cellular level proinflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 were reduced.
Anti-inflammatory
Eucalyptol was able to mediate paw oedema and granulomas in a mice model. Eucalyptol was proven to lessen the effects of rhinosinusitis in a clinical trial. In regards to acute pancreatitis eucalyptol effectively reduced cerulein-induced histological damage, pancreatic edema, NF-κB expression, levels of MPO activity and MDA, while replenished the GSH depletion. Eucalyptol was also effective against colitis in rats upon induction by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS). A marked reduction in gross damage scores and wet weights of colonic segments were shown in rats pre-treated with the terpene.
- 1,8-cineole (eucalyptol), a monoterpene oxide attenuates the colonic damage in rats on acute TNBS-colitis
- 1,8-cineole (eucalyptol) ameliorates cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis via modulation of cytokines, oxidative stress and NF-κB activity in mice
- Therapy for Acute Nonpurulent Rhinosinusitis With Cineole: Results of a Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial†
- Antiinflammatory and antinociceptive effects of 1,8-cineole a terpenoid oxide present in many plant essential oils
Anti-oxidant
Eucalyptol eluted to lessening the effects of cupric ion-mediated oxidation of lipoproteins, while simultaneously enhancing ferric ion removal ability in high-density lipoprotein. Also less lipids were found in the bloodstream in a fish model. This can also prove useful in mitagating arteriosclerosis.
Anti-cancer
Apoptosis of human leukemia Molt 4B and HL-60 cells was induced by eucalyptol. Morphological changes showing apoptotic bodies and fragmentations of DNA were observed. Also in human colon cancer cell lines HCT116 and RKO eucalyptol was effective as evidenced by WST-8 and BrdU assays. Through inactivation of survivin and Akt, and activation of p38, these molecules induced cleaved PARP and caspase-3, ending in apoptosis.
- Specific induction of apoptosis by 1,8-cineole in two human leukemia cell lines, but not a in human stomach cancer cell line
- Antitumor effect of 1, 8-cineole against colon cancer
Anti-asthma
In a lymphocyte and monocyte cell lines, eucalyptol significantly inhibited cytokine production of TNF-α, IL-1, IL-4, and IL-5. This can be inferred to control airway mucus hypersecretion by cytokine inhibition which would also be effective for sinusitis and COPD. There was also a clinical trial that found eucalyptol to be effective as well.
CBD Oils Containing Eucalyptol

Alpha Bisabolol
EFFECTS: Analgesic, Anti-cancer, Anti-inflammatory, Antifibrosis, Antifungal, Antocoagulant, Drug Potentiator.
Learn about Alpha Bisabolol »

Alpha Pinene
EFFECTS: Anti-bacterial, Anti-cancer, Anti-inflammatory, Bronchodilator, Memory Enhancer.
Learn about Alpha Pinene »
Beta Caryophyllene
EFFECTS: Analgesic, Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant, Gastric-protective.
Learn about Beta Caryophyllene »
Beta Pinene
EFFECTS: Expectorant, Bronchodilator, Anti-inflammatory, Antiseptic.
Learn about Beta Pinene »
Borneol
EFFECTS: Analgesic, Anti-cancer, Anti-inflammatory, Antifibrosis, Antifungal, Antocoagulant, Drug Potentiator.
Learn about Borneol »
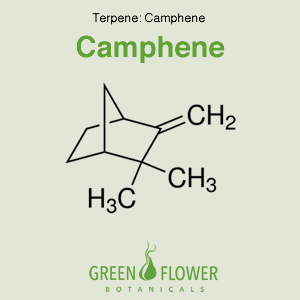
Camphene
EFFECTS: Hypolipidemic, Anti-bacterial, Antifungal.
Learn about Camphene »
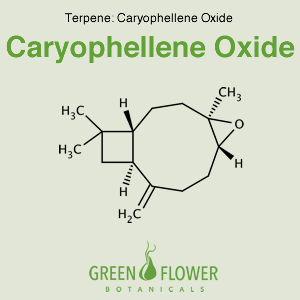
Caryophyllene Oxide
EFFECTS: Antifungal, Antocoagulant.
Learn about Caryophyllene Oxide »

Eucalyptol
EFFECTS: Anti-Alzheimer's, Anti-Asthma, Anti-bacterial, Anti-cancer, Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant.
Learn about Eucalyptol »
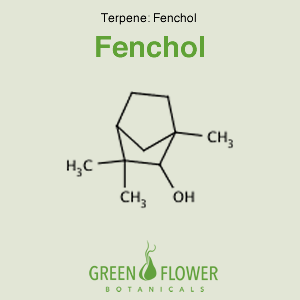
Fenchol
EFFECTS: Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, Antifungal.
Learn about Fenchol »

Humulene
EFFECTS: Anti-bacterial, Anti-cancer, Anti-inflammatory.
Learn about Humulene »

Limonene
EFFECTS: Anti-anxiety, Anti-cancer, Anti-inflammatory, Antidepressant.
Learn about Limonene »

Linalool
EFFECTS: Analgesic, Anti-anxiety, Anti-inflammatory, Anticonvulsant, Sedative.
Learn about Linalool »

Myrcene
EFFECTS: Analgesic, Antioxidant, Sedative.
Learn about Myrcene »

Nerolidol
EFFECTS: Antiprotozoan, Topical Drug Enhancer.
Learn about Nerolidol »
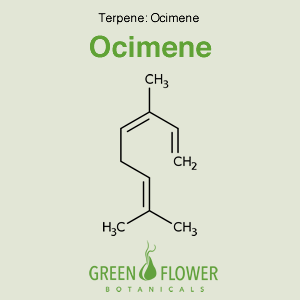
Ocimene
EFFECTS: Anti-inflammatory, Antifungal, Antiviral.
Learn about Ocimene »
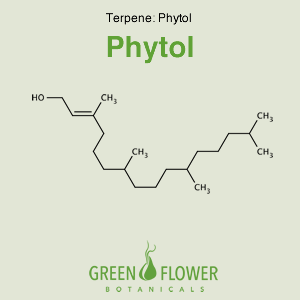
Phytol
EFFECTS: Antischistosomal, Anti-cancer, Hypolipidemic, Antidiabetic.
Learn about Phytol »

Pulegone
EFFECTS: Expectorant.
Learn about Pulegone »

Terpineol
EFFECTS: Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Anti-cancer, Sedative, Anti-inflammatory.
Learn about Terpineol »

Terpinolene
EFFECTS: Anti-bacterial, Anti-cancer, Antioxidant, Sedative.
Learn about Terpinolene »

Valencene
EFFECTS: Anti-inflammatory.
Learn about Valencene »
